On February 12, NASA announced that it would place two satellites between Earth and the Sun, with the mission's objective being to understand the connection between the Sun and Earth, and how the Sun affects the space environment in some way. Two satellites, Multi-Slit Solar Explorer (MUSE) and Helioswarm, have been selected for this science mission, these satellites will help in understanding the space environment, it will provide our deep insight on the universe, and in a way, spacecraft like Satellites and GPS will provide important information to help protect communication signals.
Thomas Zurbuchen, associate administrator for NASA, says that MUSE and the helioswarm will provide us with new and deeper insights into the solar atmosphere and space weather, adding, "These missions will not only expand the science of our other heliophysics missions, Rather, it will also provide a unique perspective and a novel approach to understanding the mysteries of the Sun.
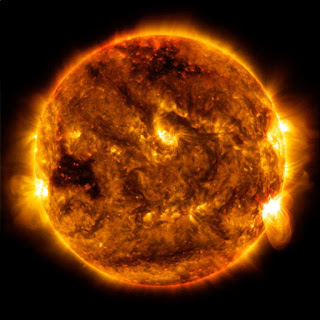
The purpose of the launch to MUSE is that it will help to understand the forces that heat the Sun's corona and the explosions in the outer region, which is responsible for space weather. A multi-slit spectrometer instrument will be coupled with MUSE, using the multi-slit spectrometer to provide deeper insight into the physics of the solar atmosphere, and obtain the highest resolution images ever taken of the solar transition region and corona.
MUSE will also provide communication with future satellites and existing satellites, and complementary observations from heliophysics research such as the Ultraviolet Spectroscopic Telescope and ground-based observatories.
The primary goal of the MUSE mission is to investigate the causes of the Sun's corona heating and instability, and to gain insight into the basic plasma properties of the corona, such as flares and coronal mass ejections. MUSE will obtain high-resolution images of the evolution of the solar flare ribbon, in a field of view focused on a large and active region of the Sun.
Thomas Zurbuchen, associate administrator for NASA, says that MUSE and the helioswarm will provide new and deeper insights into the solar atmosphere and space weather, "This mission will not only expand the science of our other heliophysics missions, but it will also help us understand the mysteries of the slain star." It will also provide a unique perspective and a novel approach.
The helioswarm mission, which will consist of nine spacecraft working together, will form constellations or "swarms", the first multiscale in-space measurements of magnetic field fluctuations and solar wind disturbances. will work to measure the speed of the known solar wind. The outer layer of the Sun is called the atmosphere, where the heliosphere covers a large area of the Solar System. Solar winds propagate through the heliosphere, and interact with the planetary magnetosphere, and disruptions such as coronal mass ejections affect their turbulence.
Studying the turbulent solar wind over a large area first requires measuring the plasma in different parts of space, with the heliosphere having eight small satellites, which together will maintain radio contact with each other. Helioswarm will consist of a hub spacecraft and eight co-orbiting small satellites, all of which will be operated via the NASA Deep Space Network with radio connectivity hub spacecraft and spacecraft communication antennas.


Comments